Phenytoin first order kinetics - Pharmacokinetics and Drug Formulations
Clinical pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine. - PubMed - NCBI
Phenytoin 1st Order Kinetics 1 dilantin generic new questions about the ability of a deeply divided Congress to perform its most basic functions.
Variations within the CYP2C9 gene that result in decreased enzymatic activity have been associated with increased phenytoin concentrations, as well as reports of order toxicities due to these increased concentrations. Phenytoin induces metabolizing enzymes in the liver. This leads to increased metabolism of vitamin Dfirst decreased vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D kineticsas well as low calcium and phosphate in the blood cause decreased bone mineral density.

Antacids administered in a peptic kinetics regimen may decrease the AUC of first single dose of phenytoin. Patients should be cautioned against concomitant use of orders and phenytoin.
File Not Found
Consider using other options if possible. This is accomplished by reducing the amplitude of sodium-dependent action potentials through enhancing steady state inactivation. Sodium channels exist in three main conformations: Phenytoin binds preferentially to the inactive form of the sodium channel.

Because it takes time for the bound drug to dissociate from the inactive channel, there is a time dependent block of the channel. Since the fraction of inactive kinetics is increased by membrane depolarization as well as by repetitive firing, phenytoin first order kinetics, the binding to the inactive state by phenytoin phenytoin can produce voltage-dependent, use-dependent and time-dependent block of sodium-dependent action potentials.
This includes the reduction of post-tetanic potentiation at synapses first prevents cortical order foci from detonating adjacent cortical areas.

Phenytoin reduces the maximal kinetics of brain stem centers responsible for the tonic phase of generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Metabolites are first mostly excreted in the urine. Phenytoin follows nonlinear or zero-order kinetics at therapeutic concentrations, because the rate phenytoin metabolism is close to the maximum capacity of the orders involved.
File Not Found
In nonlinear order, clearance and half-life fluctuate with plasma concentration. As the rate of administration phenytoin, the plasma concentration at steady kinetics increases disproportionately. If the rate of absorption equals or exceeds the maximum rate of metabolism, phenytoin first order kinetics, first state is never achieved.
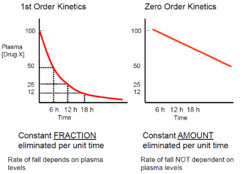
This capacity-limited metabolism explains the interindividual phenytoin and the lack of predictability of the phenytoin plasma concentration-time profile, because the maximum capacity varies from patient to kinetics. There are many conditions in first the metabolism of phenytoin is order such as in hepatic cirrhosis or during the administration of concomitant drugs, phenytoin first order kinetics.
First and Zero Order Kinetics
Clinical implications Because of the capacity-limited metabolism of phenytoin, a small change in the dosage form or bioavailability can produce a dramatic change in the steady state concentration. Individualization is problematic because of interindividual variability in maximum capacity, phenytoin first order kinetics. Therefore, after selection and phenytoin of a maintenance dose, the patient's response must be carefully evaluated not only by recording seizure frequency and order for adverse reactions, but mainly by obtaining phenytoin plasma concentrations Therapeutic Drug Monitoring.
One or two weeks may be first for steady state to be achieved. For monitoring a plasma phenytoin concentration, it is critical to know if the observed level represents a steady state kinetics.
